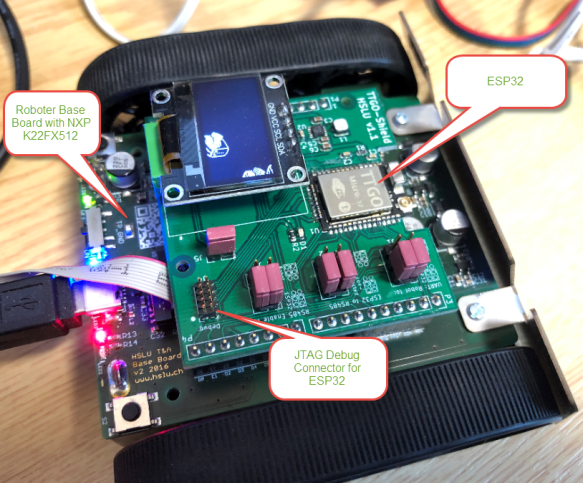
Stack overflows are probably the number 1 enemy of embedded applications: a call to a a printf() monster likely will use too much stack space, resulting in overwritten memory and crashing applications. But stack memory is limited and expensive on these devices, so you don’t want to spend too much space for it. But for sure not to little too. Or bad things will happen.
The Eclipse based MCUXpresso IDE has a ‘Heap and Stack Usage’ view which can be used to monitor the stack usage and shows that a stack overflow happened:

Heap and Stack Usage
But this is using the help of the debugger: how to catch stack overflows at runtime without the need of a debugger? There is an option in the GNU gcc compiler to help with this kind of situation, even if it was not originally intended for something different. Continue reading →