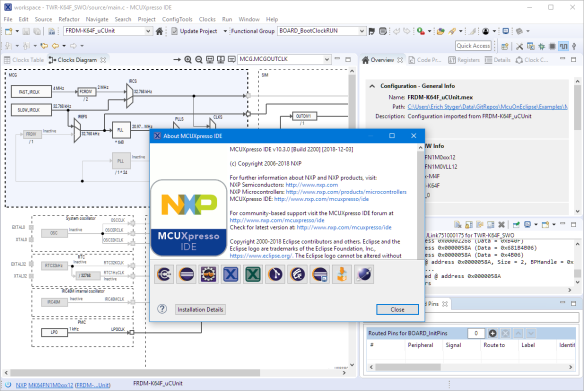
Friday this week NXP has released a new version of their flagship IDE: the MCUXpresso IDE V10.3.0. The version number indicates an incremental update from the earlier V10.2.1, but there are many exciting features and new features which make me switch my lecture material to this new IDE for the next semester.
Category Archives: Eclipse
Playing Zork with FreeRTOS on ARM in three different Ways
You might wonder what ‘Zork‘ is? Zork is one of the first and earlist fictive computer games, written around 1977 and 1979, written in MDL on a DEC PDP-10 by members of the MIT Dynamic Modelling group (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zork). I believe the first time I have played Zork was around 1984 on a Commodore 64.
Using GDB Server Monitor Commands from Eclipse GDB Console
With Eclipse as IDE it is very easy to debug an application on a board. Still sometimes it is useful to get one level down and control the GDB server directly.
Tutorial: Git with Eclipse
There are things which are game changer in the world of software development: one such event was when I started using a VCS (Version Control System): it changed for me how I keep and store my projects and settings. It even changed the way how I deal with non-software related items like documents or other valuable things: I started storing them in to a VCS too.

McuOnEclipse Components: 30-Sept-2018 Release
I’m pleased to announce a new release of the McuOnEclipse components, available on SourceForge. This release includes several bug fixes, extra support for the NXP S32 Design Studio and SDK and includes FreeRTOS V10.1.1.
Continue reading
Tutorial: First Steps with Embedded Artists NXP i.MX RT1052 OEM Module
Not ready for the complexity of a full blown Embedded Linux, but need that extra compute performance? Need an ARM Cortex-M7 running at 600 MHz module on a half-sized business card, ready to be integrated? Here we go: the Embedded Artists i.MX RT1052 OEM module:
Compute modules are very common in the Embedded Linux space, for example see this Toradex module. The reason is simple: these high-performance boards simplify the design, as I don’t have to care about the BGA packages and the external SDRAM and FLASH devices: everything is on a module I can easily integrate into my base board.
Tutorial: Open-Source Embedded GUI Library LittlevGL with i.MX RT1050-EVK
Most embedded projects need an user input device. For the NXP i.MX RT1050-EVK board I have recently added a 480×272 full color touch LCD (see “Adding a Rocktech Capacitive Touch LCD to the NXP i.MX RT1052 EVK“). I have looked at different commercially available GUI libraries, but none of them really were matching my expectations: either very expensive or closed source, or an overkill for small LCDs and projects. But then I have found LittlevGL: free-of-charge, open source, easy to use, well documented and has everything I need. And it really looks gorgeous 🙂
Tutorial: Catching Rogue Memory Accesses with ARM Watchpoint Comparators and Instruction Trace
In my “Tutorial: Catching Rogue Memory Accesses with Eclipse and GDB Watchpoints” I have used Eclipse/CDT and GDB watchpoints. I used a conditional watchpoint, but this comes with a performance hit. In this article I show how to use the ARM Cortex trace hardware to catch specific writes to a memory location. Without severe performance degradation. But for this I need a little helper: the DEADBEEF catcher!
Tutorial: Catching Rogue Memory Accesses with Eclipse and GDB Watchpoints
Eclipse is great: it gives me the tools and capabilities to solve the really hard bugs to find. An example of that ‘hard’ category are ‘rogue’ memory accesses: something in the application is accessing an unwanted memory location and corrupts the data. This might be very sporadic, or takes a long while until it happens. With normal ‘stop-mode’ debugging (setting a normal breakpoint) and stepping usually won’t let me find that bug, as it might be coming from a pointer somewhere. Maybe from an interrupt routine. Or maybe an unitialized or corrupted pointer corrupts to my memory. Usually all what I know is the memory adddress of the data, maybe what is written, but not what or who is writing to that location.
In this article I’m using one of the ‘less-known’ debugging techniques available in Eclipse and CDT and how it works: watchpoints!
In this article I’m using one of the ‘less-known’ debugging techniques available in Eclipse and CDT and how it works: watchpoints!
First Steps with the NXP i.MX RT1020 EVK Board
Powerful ARM Cortex-M7 microcontroller are on the rise, bridging the gap between traditional microcontroller and Embedded Linux systems. I already published articles for the NXP i.MX RT1052 which is an ARM Cortex-M7 running at 600 MHz. Because the RT105x is available in BGA196 package only, I have as oredered the i.MX RT 1050 EVK which has a similar device on it, but in LQFP package: