In “Tutorial: MCUXpresso SDK with Linux, Part 1: Installation and Build with Maked” I used cmake and make to build the SDK application. In this part I’m going to use the command line gdb to debug the application on the board.
Tag Archives: FRDM-K64F
Tutorial: MCUXpresso SDK with Linux, Part 1: Installation and Build with Make
I admit: my work laptop machine is running a Windows 10 OS by default. But this does not prevent me running Linux in a Virtual Machine (VM). Each host platform has its benefits, and I don’t feel biased to one or the other, but I have started using Ubuntu more and more, simply because I have worked more on Embedded Linux projects. While I have used mostly Windows with Eclipse for NXP LPC, Kinetis and i.MX platforms in the past, I started using Ubuntu too from last year with the NXP MCUXpresso SDK. I did not find much documentation about this on the web, so I thought it might be a good idea to write a tutorial about it. So here we go…
Be aware: Floating Point Operations on ARM Cortex-M4F
My mantra is *not* to use any floating point data types in embedded applications, or at least to avoid them whenever possible: for most applications they are not necessary and can be replaced by fixed point operations. Not only floating point operations have numerical problems, they can lead to performance problems as in the following (simplified) example:
#define NOF 64Continue reading
static uint32_t samples[NOF];
static float Fsamples[NOF];
float fZeroCurrent = 8.0;
static void ProcessSamples(void) {
int i;
for (i=0; i < NOF; i++) {
Fsamples[i] = samples[i]*3.3/4096.0 - fZeroCurrent;
}
}
Tutorial: Changing ARM Cortex Core or Microcontroller in Eclipse CDT Projects
Sometimes I start a project with an ARM microcontroller, and in the middle of the project I find out that it was a wrong choice at the beginning and I need to switch the microcontroller derivative or even the used ARM core. With little knowledge of the project structure and the files needed, such a switch is not the easiest thing, but definitely possible.
FreeRTOS: how to End and Restart the Scheduler
Most host or desktop systems (say Linux, Mac or Windows) have a normal use case where you start the operating system say in the morning and shut it down in the evening, and then you leave the machine. Embedded Systems are different: they are not attended, and they are supposed to run ‘forever’. Not every embedded system needs to run an OS (or in that world: Real-Time Operating System or RTOS), but the same applies here: after the RTOS is started, it is not intended that it will shutdown and restart. To the extend that you won’t they support the ‘shutdown’ and ‘restart’ functionality at all. In case of gathering coverage information this would be really useful:
In the case of FreeRTOS: what if I really need to shutdown the RTOS and restart it again, as by default this is not supported. This is what this article is about …
GDB All-Stop and Non-Stop Mode with LinkServer
GDB supports a mode which allows the GDB debug client to read memory while the target is running. This allows features like ‘live variables’: that way I can see the variables refreshed and changing over time without halting the target. Another functionality which comes with that feature is to check stopped threads or to see all threads in the system.
Using GDB Server Monitor Commands from Eclipse GDB Console
With Eclipse as IDE it is very easy to debug an application on a board. Still sometimes it is useful to get one level down and control the GDB server directly.
Using Multiple Memory Regions with the FreeRTOS Heap
ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers can have multiple memory controllers. This is a good thing as it allows the hardware to do multiple parallel memory read/writes. However this makes the memory map more complicated for the software: it divides the memory into different regions and memory segments. This article is about how to enable FreeRTOS to use multiple memory blocks for a virtual combined memory heap:
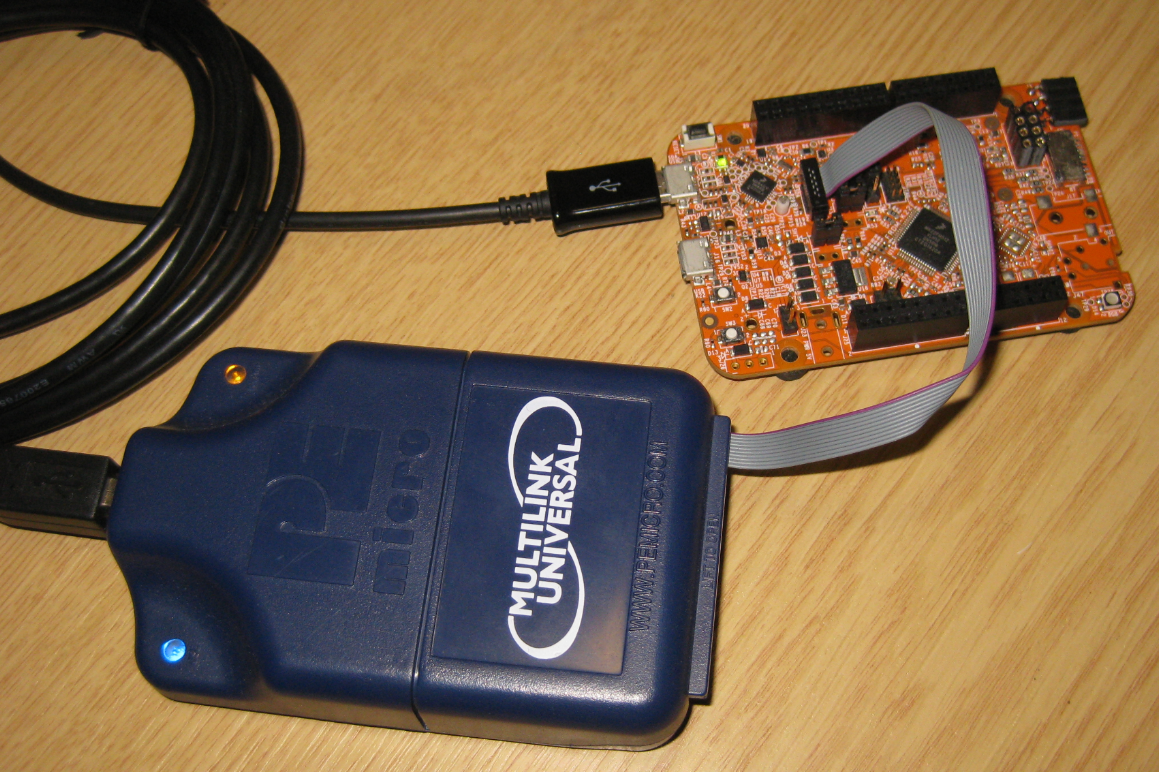
Recovering and Updating the NXP OpenSDA Bootloader with P&E Multilink and MCUXpresso IDE
Many of the NXP OpenSDA boot loaders are vulnerable to Windows 8.x or Windows 10: write accesses of Windows can confuse the factory bootloader and make the debug firmware and bootloader useless. In this post I show how to recover the bootloader using MCUXpresso IDE and the P&E Universal Multilink.
Using the LPCXpresso V2/V3 Boards to Debug an external Board
The MCUXpresso IDE (see “MCUXpresso IDE: Unified Eclipse IDE for NXPs ARM Cortex-M Microcontrollers“) has one great feature: it includes debug support for the popular LPC-Link2 debug probes. That way I have yet another powerful debug probe with extra features for ARM based boards. That LPC-Link2 circuit is present on many LPCXpresso boards from NXP. So why not using it to debug it my custom hardware?