This is the second part describing how to use DevContainer for embedded applications with VS Code.
In Optimizing Embedded Development with VS Code and DevContainer I use VS Code with a docker ‘development’ container. The container is created with a recipe to install the development tools and SDK. With VS Code and DevContainer I have the same developer experience as I would develop locally on the host.
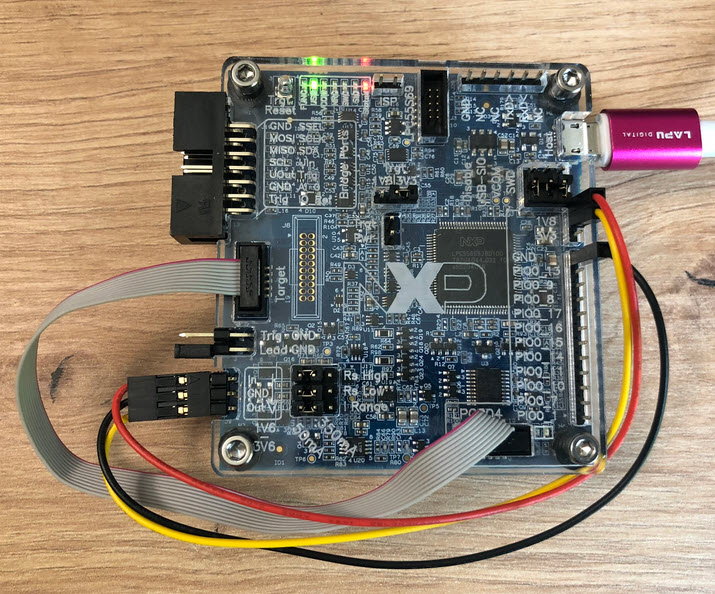
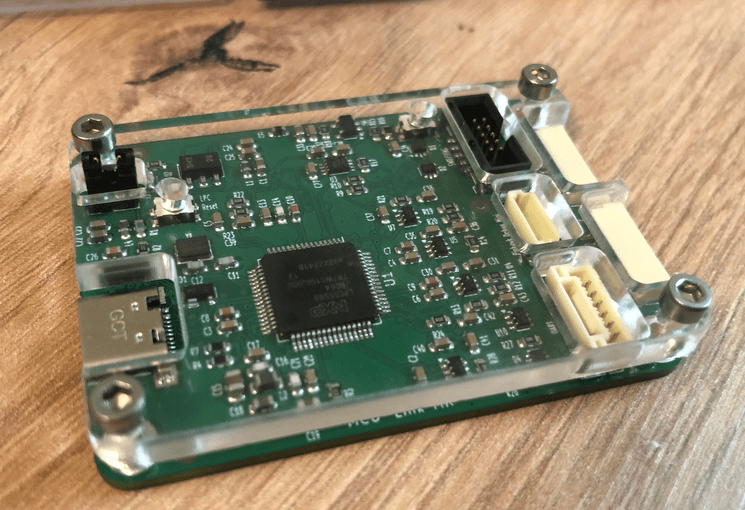
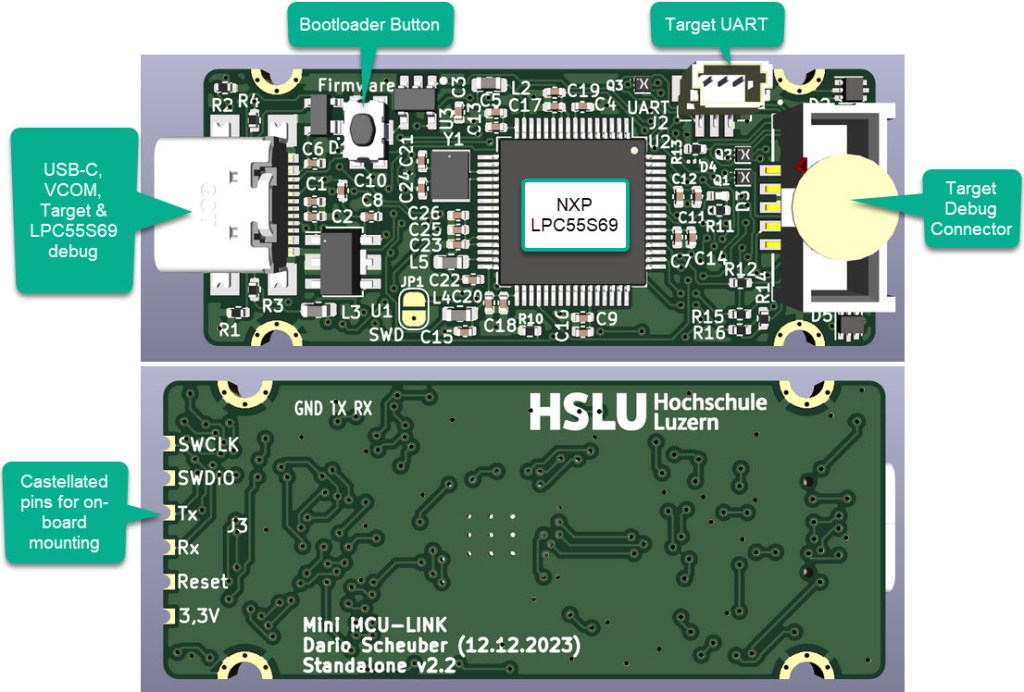
One thing not addressed in that earlier article is debugging. Using USB debug probes like a SEGGER J-Link or NXP MCU-Link is a challenge inside a container. This applies to any other debug probe as well.
The solution is to transform an USB based debug probe into one with a network connection:

In this article, I show how to do this.
Continue reading