In this short article I show you how to enable one of the hidden gems in Eclipse: how to get a description of the library function used in the code
Category Archives: Eclipse
Tutorial: Using Runtime Statistics with Amazon FreeRTOS V10
FreeRTOS includes a nice feature to give me information about how much time every task is spending running on the system:
This tutorial explains that FreeRTOS Runtime Statistics feature and how it can be turned on and used.
MCUXpresso IDE 10.2.1
NXP has just released the 10.2.1 update of their flagship Eclipse based IDE. While the number increase from 10.2.0 to 10.2.1 indicates a minor release, there are a several things which make me move over to that new release.
Debug the Last Launched Application with Eclipse and other Debug Tricks
My usual workflow is: edit – build – debug and repeat. And this for the same project again and again. So here are a few tips how to make these iterations faster with Eclipse. One thing is to use the F11 shortcut to debug the last launched/debugged application:
Porting Processor Expert Projects to MCUXpresso IDE
The McuOnEclipse GitHub repository hosts many Processor Expert projects and is very popular (cloned more than 1000 times, thank you!). Processor Expert is a powerful framework which generates driver and configuration code, simplifying application development for a wide range of microcontroller and families. But Processor Expert won’t be developed further by NXP and is not part of MCUXpresso IDE. While it is possible to install Processor Expert into MCUXpresso IDE 10.2, how can these projects used ini an IDE *without* Processor Expert? This article describes how to port an existing Processor Expert project into the NXP MCUXpresso IDE.
Show Eclipse Project Location in System Explorer
How can I open a project folder location in the system explorer?
Starting with Eclipse Oxygen, the project properties have a button for this in the Resource settings:
Using custom FreeRTOS with S32K SDK and OSIF for ARM
In “Tutorial: FreeRTOS 10.0.1 with NXP S32 Design Studio 2018.R1” I showed how to use a custom FreeRTOS with the S32 Design Studio (ARM). The OSIF (OS Interface) provides an operating system and services abstraction for the application which is used by other S32K SDK components:
Execute-Only Code with GNU and gcc
“There is no ‘S’ for Security in IoT” has indeed some truth. With all the connected devices around us, security of code should be a concern for every developer. “Preventing Reverse Engineering: Enabling Flash Security” shows how to prevent external read-out of critical code from device. What some microcontroller have built in is yet another feature: ‘Execute-Only-Sections‘ or ‘Execute-Only-Memory‘. What it means is that only instruction fetches are allowed in this area. No read access at all. Similar like ‘read-only’ ‘execute-only’ it means that code can be executed there, but no other access from that memory is allowed.
In this article I describe the challenges for a toolchain like the GNU gcc, and how to compile and link code for such an execute-only memory.
Creating Disassembly Listings with GNU Tools and Eclipse
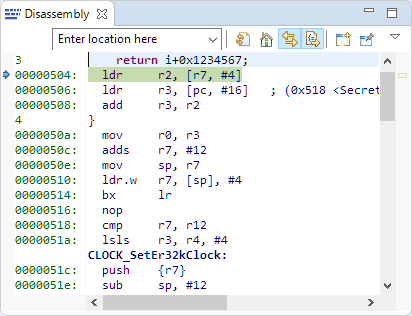
In many cases it is very useful to see the generated assembly code produced by the compiler. One obvious way to see the assembly code is to use the Disassembly view in Eclipse:
But this requires a debug session. An easier way is to use command line options to generate the listing file(s).
Eclipse Debugging with Pointers and Arrays
In the C programming language it is good practice to pass values by reference (using a pointer), especially for large set of data. For example the following function takes a message string and pointer to integer data which then is printed to the console:
static void printData(const char *msg, const int *intBuf, size_t bufSize) {
puts(msg); /* print message */
for(int i=0; i<bufSize;i++) {
printf("buf[%i] = %i\n", i, intBuf[i]);
}
}